Urethral Stricture
The urethra’s main job in males and females is to pass urine outside the body. This thin tube also has an important role in ejaculation for men. When a scar from swelling, injury or infection blocks or slows the flow of urine in this tube, it is called a urethral stricture. Some people feel pain with a urethral stricture.
SYMPTOMS
When a stricture is narrow enough to decrease urine flow, you will have symptoms. Problems with urinating, UTIs, and swelling or infections of the prostate may occur. Severe blockage that lasts a long time can damage the kidneys. Some symptoms are:
- Slow or decreased urine stream
- Spraying of urinary stream
- Pain while voiding
- abdominal pain
DIAGNOSIS – BY URETHROSCOPY
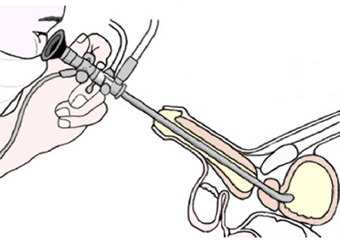
The doctor gently places a small, lubricated scope (a small viewing instrument) into the urethra. It is moved up to the stricture. This lets the doctor see the narrowed area. This is done in the office and helps your doctor decide how to treat the stricture.
DIAGNOSIS – BY RETROGRADE URETHROGRAM
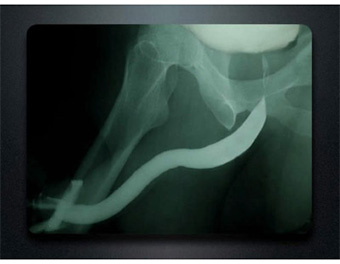
This test is used to see how many strictures there are, and their position, length and severity. This is done as an outpatient X-ray procedure. Retrograde in this case means “against the flow” of urine. Contrast dye (fluid that can be seen on an X-ray) is inserted into the urethra at the tip of the penis. No needles or catheters are used. The dye lets the doctor see the entire urethra and outlines the narrowed area. It can be combined with an antegradeurethrogram (antegrade means “with the flow” of urine). Dye inserted from below fills the urethra up to the injured area. Dye inserted from above fills the bladder and the urethra down to the stricture. These tests together let the doctor find the gap to plan for surgery.Also, if you have trauma to the urethra, you may have this X-ray procedure after emergency treatment. Contrast dye can be injected through the catheter that was placed for healing.
TREATMENT – BY DILATION
Enlarging the stricture with gradual stretching
TREATMENT – BY URETHROTOMY
Cutting the stricture with a laser or knife through a scope that is passed via the natural urinary passage
TREATMENT – BY OPEN SURGERY
Surgical removal of the stricture with reconnection and reconstruction, possibly with grafts (urethroplasty) .Graft which is usually used is the oral graft from the inner lining of the mouth or tongue or lower lip. This surgery requires a week of hospitalization. A tube will be placed inside your urinary passage and will usually remain there for 4 weeks after which it can be removed.
MEDICATIONS
Currently there are no drugs available to help treating Strictures.
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
INTRODUCTION
A UTI is when bacteria gets into your urine and travels up to your bladder. UTIs cause more than 8.1 million visits to doctors each year. About 10 in 25 women and 3 in 25 men will have symptoms of at least 1 UTI during their lifetime.
SYMPTOMS
The main symptom is burning sensation while passing urine. . You may even try to urinate but only get a few drops. At times, you may lose control and wet yourself. You may also find that your urine smells bad or is cloudy.Kidney infections often cause fevers and back pain. These infections need to be treated at once because a kidney infection can quickly spread into the bloodstream and cause a life-threatening health issue.
DIAGNOSIS
UTIs can be found by analyzing a urine sample. The urine is examined under a microscope for bacteria or white blood cells, which are signs of infection. Your doctor may also orderan urine culture. Only if the urine culture is positive for bacterial growth you will be labeled as having UTI.
Collecting urine sample :
Your doctor or another healthcare professional will give you a container and explain how you should collect the urine sample.
You can collect a urine sample at any time of day, unless your GP or practice nurse advises you otherwise.
The types of urine sample you might be asked for include a random specimen, first morning specimen or timed collection.
To collect a clean urine sample:
- Label the container with your name, date of birth and the date
- Wash your hands, (Retract prepuce for male patients / Separate labia for females)
- Start to urinate, but don’t collect the first part of urine that comes out
- Collect a sample of urine “mid-stream” (see below) in a sterile screw-top container
- Screw the lid of the container shut
- Wash your hands thoroughly
- If your doctor gives you any other instructions, follow these.
What is a mid-stream urine sample?
A mid-stream urine sample means that you don’t collect the first or last part of urine that comes out. This reduces the risk of the sample being contaminated with bacteria from urethra and the skin around the urethra (tube that carries urine out of the body)
TREATMENT
There are two types of UTIs: simple and complicated. Simple UTIs are infections that happen in healthy people with normal urinary tracts.Complicated UTIs happen in abnormal urinary tracts or when the bacteria causing the infection cannot be treated by means of only antibiotics. Most women have simple UTIs, while the UTIs in men and children should be thought of as complicated.
Simple UTI
A simple UTI can be treated with a short course of antibiotic medicines. A 3-day course of antibiotics will often treat most uncomplicated UTIs. However, some infections may need to be treated for 5 days. Depending on the type of antibiotic used, you may take a single dose per day or up to 4 doses per day. Pain and the urge to urinate often go away after a few doses, but you should still take the full course of the medicines even if you feel better. Unless UTIs are fully treated, they can often return. You should also drink plenty of liquids, especially around the time of a UTI.
Postmenopausal women with UTIs may be helped by topical (vaginal) hormone replacement (estrogen). Since some patients cannot take estrogen replacement, you should talk with your doctor before starting any treatment.
Complicated UTI
If the UTI is a complicated UTI, then a longer course of antibiotics is given and is often started intravenously (IV) in the hospital. After a short period of IV antibiotics, the antibiotics are given by mouth for up to many weeks. Kidney infections are often treated as a complicated UTI.
Simple UTIs often improve with 3 days of antibiotics and you do not need a urine culture to prove that it is gone. If you have a complicated UTI, you should have a urine culture to show that the UTI is resolved. If your symptoms don’t go away even with medication, then you may need a longer course of medicines, a different drug or different way of taking it.About 1 in 5 young women who have a UTI will have another. Men are less likely to get a UTI in the first place. But if they get one, they are likely to have another because the bacteria tend to hide inside the prostate. If you get UTIs often (3 or more per year), then you should see your doctor. Your doctor might want to do more tests (such as checking if the bladder empties) to find out why. You may also need an ultrasound or CT scan, which allow your doctor to look for any abnormalities of the urinary tract. If you keep getting UTIs, a longer course of low-dose antibiotics. There are also methods of self-testing that your health care provider may arrange that let you diagnose and treat your UTIs at home.
FAQ 1 : Why do I get UTI?
Most UTIs are single events that, if treated, will not come back. Some patients have anatomical and genetic predispositions that tend to make getting UTIs more likely.
FAQ 2 : When should I be worried?
If you are being treated for a UTI and are not getting better, or you have symptoms of a UTI along with upset stomach and vomiting, then you should contact your health care provider. If you ever see blood in your urine, you should contact your doctor right away.
FAQ 3 : Will a UTI cause damage to the kidneys?
If the UTI is treated early, then there will likely be no lasting effect on your urinary tract. UTIs can cause harm if not found and treated quickly and adequately.
FAQ 4 : What if I am pregnant?
If you are pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, then you should call your doctor right away. UTIs during pregnancy can put both mother and baby at risk if not dealt with quickly and properly.
Kalyani Kidney Care Centre, besides providing kidney disease treatment, specializes in treating Urethral Stricture and UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) as well


